Everything old is new again: How fresh eyes in the operatory could save lives
Is it possible that our patients would be better served if we observed characteristics we assess on a daily basis through a fresh, clear lens? With the beginning of the New Year, we can achieve this one goal as a team of dental professionals.

Is it possible that our patients would be better served if we observed characteristics we assess on a daily basis through a fresh, clear lens? With the beginning of the New Year, we can achieve this one goal as a team of dental professionals.
Dental hygienists have a reputation for being an observant group of people. All you have to do is ask any partner of a dental hygienist. They and others go as far as to joke about the “hygiene gene.”
We are accustomed to detecting traits and symptoms without being aware. At a restaurant, a dental hygienist will notice the server’s teeth even before cracking open a menu. This year, let’s look at our assessments, how we speak to patients, and look to a multidisciplinary approach when it comes to referring to specialists more often. We have the power to help people live healthier, happier lives going far beyond brushing and flossing.
Trending article: 4 things dental hygienists don't like to hear
We frequently speak about the oral-systemic link, yet our patients are struggling to breathe before our very loupes! I know that for much of my 38 years of practicing dental hygiene, I have been guilty of dutifully noting “abnormalities” in the chart. “Yes, we’ll just watch this,” is the message we frequently relay to patients. We have focused on important restorative, orthodontic and periodontal assessments. Of course these aspects are critical in our practice of dental hygiene and we should never dismiss them. In addition, I think we can all agree that breathing is paramount to sustaining life.
Three things we frequently note, seldom refer and infrequently look for origins of are:
- Scalloped tongue: This can be a sign of low tongue posture in the mouth contributing to complications for swallowing. It can also be an indicator of sleep apnea where a patient breathes shallowly and even pauses many times in their breathing for a period of time during sleep, thus starving the brain of much needed oxygen.1
- Tongue thrust: This is also referred to as a reverse swallow. The tongue pushes against the front teeth in an outward motion. A tongue thrust can contribute to orthodontic relapse and sleep apnea, contributing to a compromise of airway patency.2
- Bruxism: Recent studies indicate that bruxism during sleep is a marker for sleep apnea. The body subconsciously is using the jaw to align itself to open the airway in order to keep a person breathing.3,4
All of these may be symptoms of a serious, deeper, underlying issue: a restricted airway. We have the ability to save not only teeth, but also lives if we consider causes instead of only symptoms. Using a multidisciplinary approach can potentially save our patients’ lives. A multidisciplinary approach is imperative in a patient centric practice.
When we ask patients if they would like to learn more about what our examination means, and they become educated, the next natural question for them is, “What can be done to help this?” We have the knowledge and expertise to advise them.
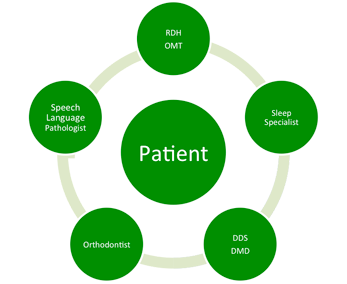
The dental team is on the front line when it comes to evaluating patients and considering the root cause of symptoms. Some of what we assess may be significant for comorbidities such as orofacial myofunctional disorder (OMD) and orthodontic malocclusion. As dental hygienists, we can help to raise the level of care in dental practices by discussing with the dentist a protocol for referring to sleep specialists, orofacial myofunctional therapists (OMT), oral surgeons and orthodontists, according to our findings. We can stress the importance of this multidisciplinary approach in treating our patients.
Trending article: The importance of combatting antimicrobial resistance
If a dental practice is not interested in creating a protocol, we clinicians, without diagnosing, are able to suggest to patients that they have a discussion with their physician to discuss our findings.
May this be the year that we not only see and take note, but that we help to save lives. Let’s begin by using a collaborative approach in our practice and refer to appropriate specialists in order to treat underlying causes of the symptoms we evaluate every day. By considering characteristics that we have always noted, but in a new way, we will continue to give the highest quality of care to our patients.
Sources
1 Rinaldi V. Sleep-Disordered Breathing and CPAP: Overview of Sleep-Disordered Breathing, Pathophysiology of SDB, Etiology of SDB. Emedicine.medscape.com. 2016 [cited 5 January 2016]. Available from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/870192-overview#a6
2 Proceedings of the American Thoracic Soc. 2008 Feb 15; 5(2): 144–153.
3 Sleep Med Nov. 2002; 3(6):513-515.
4 Cranio. 2015 Dec 29:1-5.