Study Reveals Link Between Interdental Cleaning and Blood Glucose Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
This study from Sunstar and the Clinic Masae Minami/Minami Diabetes Clinical Research Center shows the clear link between good oral health care and lower blood glucose levels.
Study Reveals Link Between Interdental Cleaning and Blood Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Image credit: © Sunstar
A recent cross-sectional study has found a connection between good oral hygiene practices, specifically interdental cleaning, and improved blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Conducted by the Clinic Masae Minami/Minami Diabetes Clinical Research Center in collaboration with Sunstar, an international oral health care company, the research emphasizes the significance of maintaining oral health for better glycemic control in diabetic patients.
The study took a look at the oral hygiene habits and blood sugar control indicators of 104 type 2 diabetes patients with 15 or more natural teeth. It highlighted a significant correlation between interdental cleaning habits and 24-hour blood glucose fluctuations, shedding light on the impact of preventive dental care in managing blood glucose levels.
The study's methodology involved comprehensive assessments, including oral hygiene habits, blood and urine tests for various glycemic control indicators, and analysis of continuous glucose monitoring data, shedding light on the detailed relationship between oral care and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients.
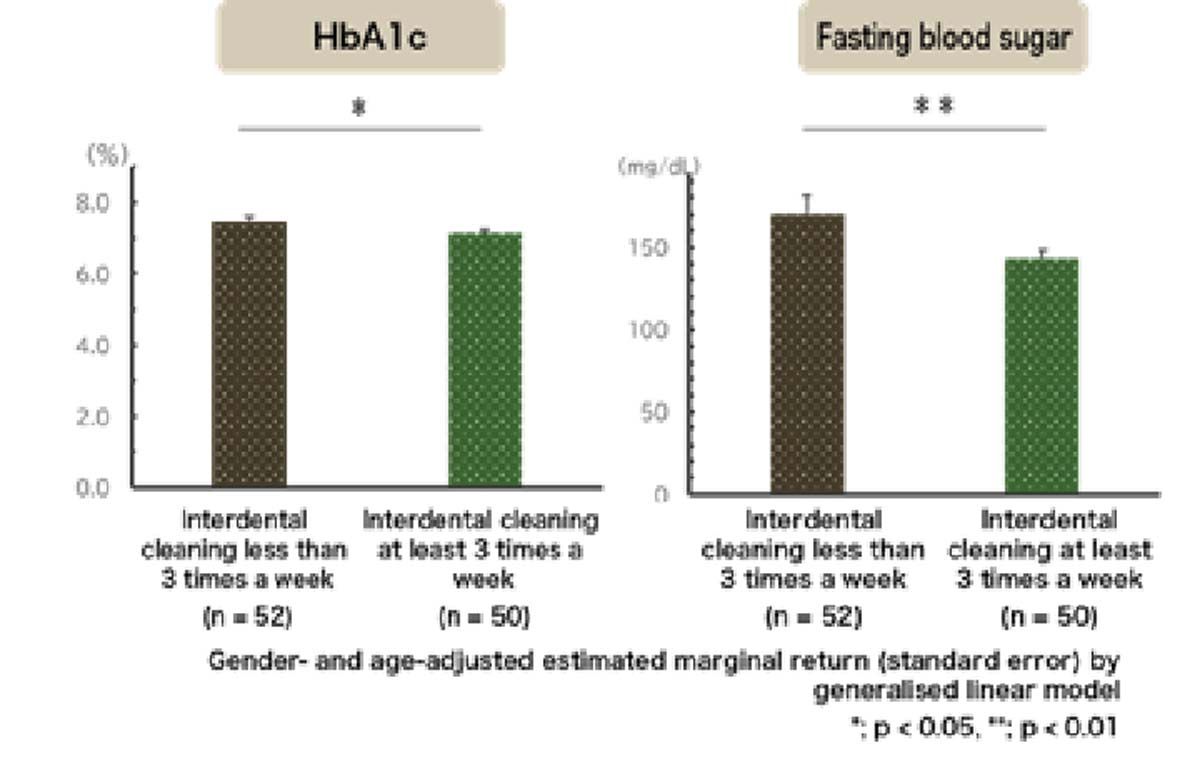
One of the standout revelations was the correlation between the frequency of interdental cleaning and the duration spent in the target blood glucose range of 70-180mg/dL during a 24-hour period, known as Time in Range. Patients who engaged in interdental cleaning at least 3 times per week exhibited lower average glucose levels and a higher Time in Range compared to those who did not maintain this oral hygiene practice.
The findings also highlighted the association between the number of teeth and oral hygiene practices, linking them to key glycemic control parameters like HbA1c and fasting blood sugar levels. This study adds weight to previous research demonstrating the interconnection between diabetes and periodontal disease, underscoring the positive impact of managing periodontal health on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients.
The study's outcome, presented at the 66th Annual Scientific Meeting of the Japan Diabetes Society, indicates that while a direct causal relationship wasn’t established, integrating regular dental visits and interdental cleaning into oral care routines is expected not only to prevent tooth loss but also to contribute to overall health maintenance and promotion.
Sunstar's involvement in the research stems from a personal narrative, as the company's founder, Kunio Kaneda, battled diabetes, motivating Sunstar's focus on exploring the link between diabetes and periodontal disease, leading to research, new product development, and awareness initiatives in collaboration with medical institutions and universities.
This breakthrough study reinforces the critical role of oral hygiene in managing blood glucose levels for individuals with type 2 diabetes, opening avenues for holistic approaches to diabetes care that incorporate dental health as an integral component of overall well-being. To read more on the methodology and science behind the study, read it here.