Obturation: The foundation of long-term endodontic success [VIDEO]
Lateral condensation with standardized gutta percha points in combination with a root-canal sealer is a commonly accepted technique. In this method, once the master gutta percha point has been fitted, the canal is ready to be filled using subsequent points: the spreader is placed as far as possible into the canal toward the apex, and it is spread from side to side to compress the gutta percha and sealer against the walls until there is no more room for additional points.
Long-term success in endodontics relies heavily on proper obturation.
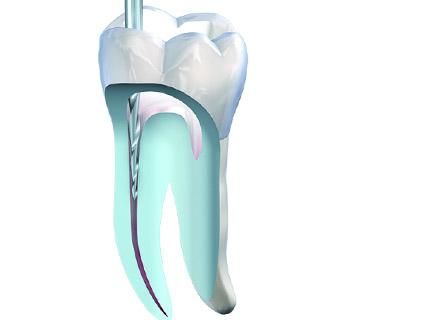
Long-term success in endodontics relies heavily on proper obturation. Once diseased pulp has been removed and the canal has been properly shaped and cleaned, it is imperative that the resulting cavity is hermetically sealed with a filling that takes on the function of the pulp to provide protection from renewed infection.
Lateral condensation with standardized gutta percha points in combination with a root-canal sealer is a commonly accepted technique. In this method, once the master gutta percha point has been fitted, the canal is ready to be filled using subsequent points: the spreader is placed as far as possible into the canal toward the apex, and it is spread from side to side to compress the gutta percha and sealer against the walls until there is no more room for additional points.
RELATED: How to remove instrument fragments with KOMET's Endo Rescue Kit
Single-cone obturation is an option that generally requires less time and material than lateral condensation. The gutta percha point must correspond to the ISO size and taper that conforms to the final root-canal preparation.
Note: Figures 1, 3, and 4 depict instruments used for the removal of diseased pulp and subsequent shaping and cleaning. The steps are explained in greater detail in the July 9 edition of Technique Geek and you can see those details here.
Clinical Sequence
Figure 1: Enlarge the entrance of the canal with the OP10L19 opener.
Figure 2: In a revision case, use the GPR gutta-percha remover following exposure of the canal access cavity. At an optimum speed of 2,000 rpm without cooling, move the instrument along the canal wall toward the apex. As soon as the gutta-percha softens, increase the speed to 4,000 rpm, and carefully guide the instrument further toward the apex. Upon withdrawal, the gutta percha adheres to the instrument for easy removal.
Figure 3: Use the PathGlider™ file to mechanically prepare the glide path.
Figure 4: Mechanically prepare the canals with the F360® or F6 SkyTaper™ root-canal preparation system.
Figure 5: Following complete disinfection and irrigation procedures, thoroughly dry the canal using the system-matched paper points for the F360…
Figure 6: …or the F6 SkyTaper system.
Figure 7: Use the F360 system-matched gutta-percha points…
Figure 8: …or the F6 SkyTaper gutta-percha points to properly fill the canal.
Figure 9: Using a red contra angle at 160,000 rpm or a turbine at 300,000 rpm, trim visible excess gutta percha with the GP 801 L gutta-percha cutter. Note: Gutta percha should first be roughly cut with a scalpel to prevent it from wrapping around the instrument.
Learn more by watching the video below...
Komet USA’s comprehensive line of endodontic instruments and accessories ensures successful treatment for all types of root-canal cases. The line includes instruments specially engineered for every step of the procedure, from straight-line access and proper cleaning, shaping, and preparation to obturation and final finishing. Each instrument complements its counterparts, working to simplify endodontic procedures and enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
For more information on Komet USA’s endodontic instruments, paper points, or gutta-percha points, contact Komet USA LLC at (888) 566-3887 or www.kometusa.com.
GrowthPlug from PracticeTek: An Inside Look with Nick Navarro
May 7th 2024Dive deep on what GrowthPlug can do for the dental practice with GrowthPlug Digital Marketing Consultant Nick Navarro. With a focus on growth, engagement, and reach, GrowthPlug aims to support dental and orthodontic practices. [1 minute]