Cementable, screw-retained or screw-mentable?
Choosing the right implant for the case can be difficult - this is what they all offer.
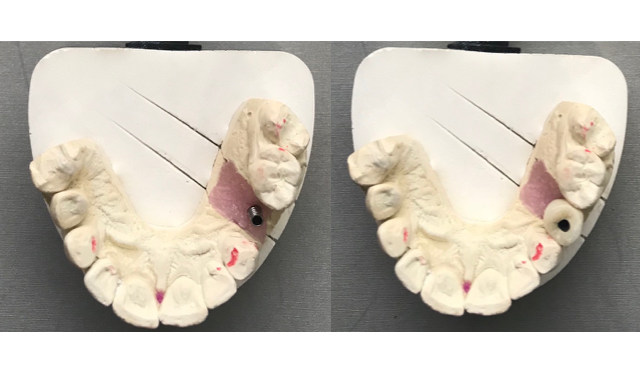
When it comes to selecting the correct implant route for your patient, different clinical situations must be considered when selecting the appropriate abutment, as the proper design and material enable the clinician to achieve an excellent clinical outcome.
It has been shown that screw and cement retained crowns generate approximately the same amount of strain at the implant site.1 The rise in popularity of both types of restorations represents the departure from the stock abutments and casting a UCLA (Universal Clearance Limited abutment). Cementable and screw-retained implant crowns have demonstrated extremely high rates of success, but they both have their advantages and disadvantages.
Cementable restorations
Advantages:
- The primary advantage of custom abutments is the ability to correct the angulation of implants. Facio-lingual bone
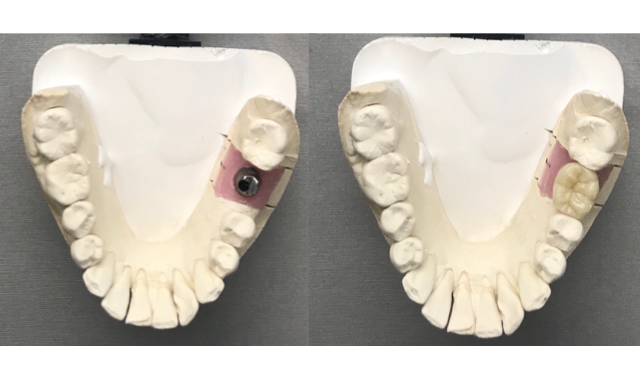
- volume can require the practitioner to orient the apical portion of the implant toward the lingual or palatal aspect. It is
common for the prosthetic platform to reside in a position that would situate the access hole of a screw-retained crown on the labial aspect of the restoration.
Disadvantages:
- The chief drawback of custom abutments is the potential residual cement, one of the main causes of peri-implantitis.2
- In case of limited vertical dimension, there may not be sufficient restorative space to accommodate the abutment height required for cement retention. At least 5 mm of abutment height is needed for proper retention of a cement-retained restoration.
Screw-retained restorations
Advantages:
- Screw-Retained crowns eliminate any concerns with cement removal. Screw-retained crowns have exhibited

- slightly fewer technical and biological complications, which may be a result of incomplete cement cleanup.2-3
- If any complications should ever arise, screw-retained crowns can be retrieved with relative ease avoiding damage to the restoration. This simplifies prosthetic maintenance and provides a measure to assess the underlying tissue when needed. Additionally, the prosthetic screw can be replaced with relative ease.
- When vertical dimension is limited, screw-retained restorations allow for a lower profile retention of the abutment system.
Disadvantages:
- Screw-retained crowns are frequently contraindicated in the anterior region due to pronounced alveolar bone reabsorption in mandible and horizontal bone loss in the maxilla.1,4 The resultant bone limitations in the anterior frequently call for implant angulation that must be corrected with a custom abutment.
- To fabricate a full ceramic screw-retained restoration, a pre-fabricated ti-base is used. These ti-bases provide less control over the depth of the margins, contours, angulation and emergence profile of the final restoration causing tissue impingement if implants are placed deeper than 3 mm.
Screw-mentable restorations
Prudental Laboratories cements a crown with open access over a custom milled titanium abutment. This method combines
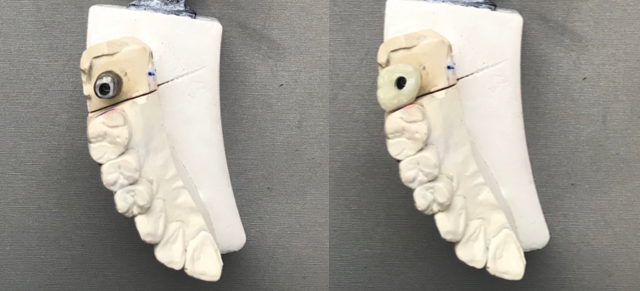
the advantages of both Cement & Screw-Retained Restorations and eliminates all the disadvantages.
Features:
- Custom Implant Angulation
- No Cement Required
- Open Access to the Crown
- None of the Restrictions of a Pre-Fabricated Ti-base
This method allows clinicians and patients to take advantage of the best of both worlds. For more information, please contact Prudental Laboratories at (800) 277 8336 or info@prudentallab.com
References:
1 - Schittenhelm B KarlM GraeF,Heckmann S TaylorT Effect of various fixation parameters on strain development of screw and cement retained implant supported restorations Quintessence INT: 2013: 441(6): 409-16 original date is "Jul-sep"
2-Korsch M,Robra BP, Walther W. Cement associated signs of inflammation: retrospective analysis of the effect of excess cement on peri-implant tissue. int J Prosthodont. 2015 Jan-Feb: 28 (1) :11-8
3 -Wittneben JG, Millen C, Braggerv. Clinical performance of screw-versus cement retained fixed implant supported reconstructions -a systematic review. Int J oral Amxillofac implants. 2014; 29 suppl: 84-98
4 -Carlsson GE, Bregman B, Hedegard B Changes in contour of Maxillary alveolar process under immediate denture. A longitudinal Clinical and X-ray cephalometric study covering 5 years Acta odontol scand. 1967 June : 25(1) :45-75
Product Bites – November 10, 2023
November 10th 2023The weekly new products podcast from Dental Products Report is back. With a quick look at all of the newest dental product launches, Product Bites makes sure you don't miss the next innovation for your practice. This week's Product Bites podcast features new launches from Amann Girrbach, DMG, Pac-Dent, and ASI Dental Specialties. [4 Minutes]
ACTIVA BioACTIVE Bulk Flow Marks Pulpdent’s First Major Product Release in 4 Years
December 12th 2024Next-generation bulk-fill dental restorative raises the standard of care for bulk-fill procedures by providing natural remineralization support, while also overcoming current bulk-fill limitations.
Product Bites – October 27, 2023
October 27th 2023Product Bites makes sure you don't miss the next innovation for your practice. This week's Product Bites podcast features new launches from Kerr Dental, MGF, PreXion, ZimVie, Amann Girrbach, VOCO, ASI Dental Specialties, DMG, and NovoDynamics. [8 Minutes]